Does Density Increase With Temperature
The density of a liquid will modify with temperature and pressure. The density of water versus temperature and pressure is indicated below:
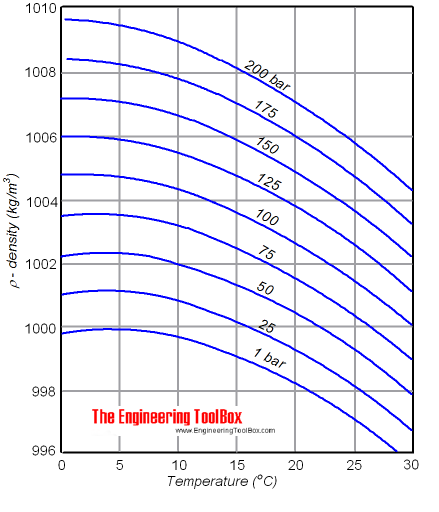
Meet too H2o - Density, Specific Weight and Thermal Expantion Coefficient, for online calculator, figures and tables showing changes with temperature.
Density
The density of a liquid can exist expressed every bit
ρ = m / V (one)
where
ρ = density of liquid (kg/kiii)
m = mass of the liquid (kg)
V = volume of the liquid (m3)
The inverse of density is specific volume:
v = 1 / ρ
= 5 / m (ii)
where
v = specific volume (thousand3/kg)
Volume and alter in Temperature
When temperature increases - most liquids expands:
dV = V1 - V0
= V0 β dt
= V0 β (t1 - t0) (iii)
where
dV = 5ane - 50 = modify in volume - difference between final and initial volume (m3)
β = volumetric temperature expansion coefficient (thousand3/miii oC)
dt = ti - t0 = modify in temperature - difference betwixt final and initial temperature (oC)
(3) can be modified to
51 = V0 (i + β (tane - t0)) (3b)
Density and modify in Temperature
With (one) and (3b) the final density after a temperature alter can exist expressed equally
ρ1 = yard / (V0 (1 + β (ti - t0))) (4)
where
ρ1 = terminal density (kg/miii)
- or combined with (2)
ρ1 = ρ0 / (one + β (tone - t0)) (4b)
where
ρ0 = initial density (kg/m3)
Volumetric Temperature Coefficients - β
- water : 0.0002 (miii/m3 oC) at 20oC
- ethyl alcohol : 0.0011 (one thousandiii/mthree oC)
- volumetric expansion coefficient for some normally used materials
Note! - volumetric temperature coefficients may vary strongly with temperature.
Density and modify in Pressure
The influence of force per unit area on the volume of a liquid can exist expressed with the three dimensional Hooke's law
E = - dp / (dV / V0)
= - (p1 - p0) / ((Vi - V0) / 50) (v)
where
E = bulk modulus - liquid elasticity (N/m2)
The minus sign corresponds to the fact that an increment in the pressure leads to a decrease in volume.
With (5) - the final book after pressure change can exist expressed as
V1 = V0 (one - (pi - p0) / E) (5b)
Combining (5b) with (1) - the final density can be expressed equally:
ρone = m / ( V0 (1 - (p1 - p0) / Due east)) (half dozen)
- or combined with (2) - the final density can be expressed as
ρone = ρ0 / (one - (p1 - p0) / E) (6b)
Bulk Modulus Fluid Elasticity some common Fluids - E
- water : 2.15 109 (N/m2)
- ethyl alcohol : 1.06 109 (N/m2)
- oil : i.5 x9 (North/1000two)
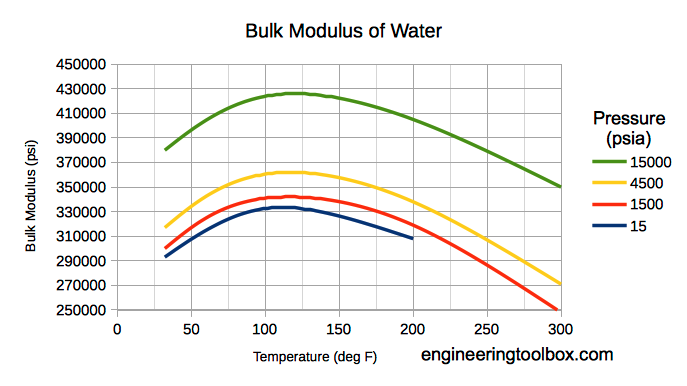
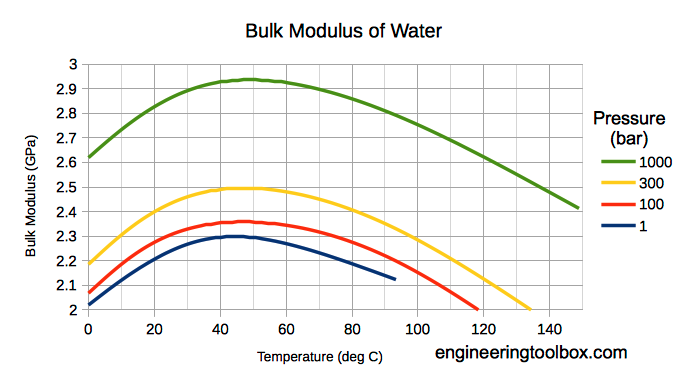
Note! Bulk modulus for liquids varies with pressure and temperature.
Bulk modulus for water - Imperial Units
Bulk modulus for Water - SI units
Density of a fluid changing both Temperature and Force per unit area
The density of a fluid when changing both temperature and pressure can exist expressed combining (4b) and (6b):
ρ1 =ρ1(from eq.1) / (i - (p1 - p0) / Due east)
= ρ0 / (1 + β (t1 - t0))/ (i - (p1 - p0) / Due east) (7)
Example - Density of Water at 100 bar and 20oC
- density of h2o 0oC: 999.8 (kg/m3)
- expansion coefficient of water at 10oC: 0.000088 (m3/m3 oC) (average value between 0 and twentyoC)
- bulk modulus of h2o:2.15 109(N/one thousandii)
Density of water can be calculated with (3):
ρ1 = (999.8 kg/yard3) / (one + (0.000088 thousand3/thousandthree oC) ((xx oC)- (0 oC))) / (1 - ((100 105 Pa) - (1 105 Pa)) / (two.fifteen 109 N/one thousand2))
= 1002.7 (kg/m3)
Does Density Increase With Temperature,
Source: https://www.engineeringtoolbox.com/fluid-density-temperature-pressure-d_309.html
Posted by: sullivanrefereall.blogspot.com


0 Response to "Does Density Increase With Temperature"
Post a Comment